
A SLAP tear labrum is a shoulder injury that can disrupt your daily life with pain and instability. This article will walk you through its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options, so you know what to expect and how to address it effectively.
Key Takeaways
- SLAP tears are specific shoulder labrum injuries commonly caused by repetitive overhead motions or acute trauma, leading to shoulder pain and instability.
- Diagnosis involves a combination of patient history, physical examinations, and imaging techniques such as MRI scans to confirm the presence of a tear.
- Treatment for SLAP tears can be non-surgical, focusing on rest and physical therapy, or surgical, involving arthroscopic repair to restore shoulder function and stability.
If you’re experiencing shoulder pain, instability, or any symptoms that might indicate a SLAP tear, it’s essential to seek professional care early. At Academy Orthopedics, our board-certified surgeons and dedicated team specialize in diagnosing and treating labral injuries with advanced techniques like arthroscopic surgery. With nearly four decades of excellence in orthopedic care, we’re here to help you regain your mobility and live pain-free. Schedule a consultation at one of our convenient locations in Cumming, Buford, or Duluth, GA, by calling (770) 271-9857 or booking online today.
👉Also Read: Choosing the Right Specialist: What Doctor Should I See for Shoulder Pain?
Understanding the Shoulder Labrum
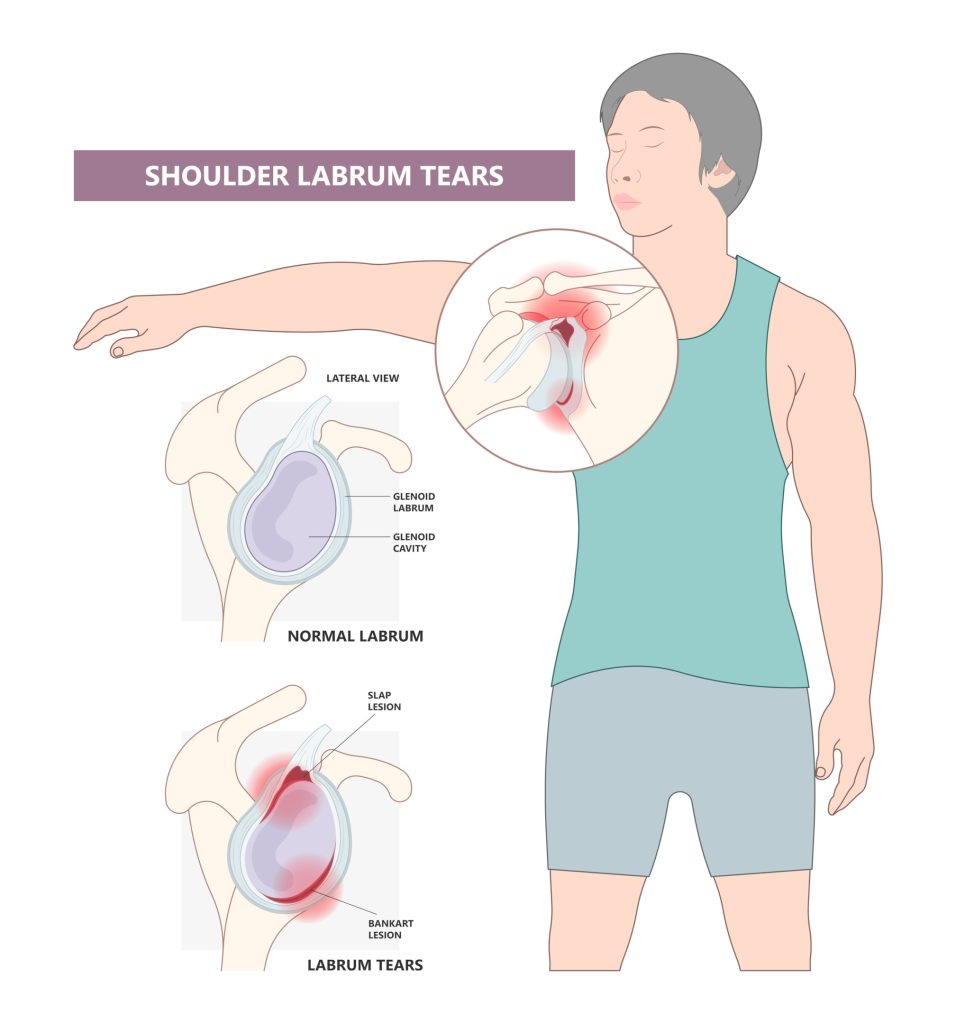
The shoulder labrum is a crucial component of the shoulder joint, playing a significant role in its stability and function. Surrounding the shoulder socket, the labrum acts as an anchor for ligaments and a cushion for the upper arm bone, ensuring smooth and stable shoulder movements.
Knowing its anatomy and function helps one understand the impact of shoulder labrum tears and a torn shoulder labrum tear.
Anatomy of the Shoulder Labrum
The shoulder labrum is a cup-shaped rim of fibrous cartilage that encircles the socket of the shoulder joint, providing a deep, stable seat for the ball of the upper arm bone. This structure is essential for maintaining the shoulder’s integrity, as it serves as an anchor point for several ligaments and the biceps tendon. The biceps tendon attaches to the labrum at the top, connecting it to the shoulder muscles and aiding in load distribution during movements.
In addition to its structural role, the labrum acts as a cushion for the upper arm bone, absorbing shocks and aiding in smooth rotations. The intricate link between the labrum, ligaments, and tendons is crucial for shoulder stability and function, so any labrum tears in the labrum are significant.
Function of the Shoulder Labrum
The shoulder labrum is indispensable in keeping the shoulder joint in place. It deepens the shoulder socket, creating a more secure fit for the upper arm bone, which prevents dislocations and enhances stability. The labrum’s role as an attachment point for ligaments further reinforces this stability, supporting the shoulder muscles in their movements and functions.
When the labrum is torn, its ability to maintain shoulder stability is compromised, leading to potential instability and a higher risk of dislocations. As a bumper, the labrum ensures the upper arm bone stays securely in the socket, essential for normal shoulder function.
What is a SLAP Tear?
A SLAP tear is a specific type of shoulder labrum tear that affects the superior part of the labrum, where the biceps tendon attaches. SLAP stands for Superior Labrum Anterior to Posterior, indicating the areas impacted by the injury.
Athletes involved in repetitive overhead motions, like baseball pitchers, can also commonly experience tears in the rotator cuff tendons, which form a significant portion of shoulder injuries.
Causes of SLAP Tears
Repetitive overhead motions in sports like baseball and softball are primary contributors to SLAP tears. These motions strain the shoulder joint, increasing the risk of a tear. Acute trauma, such as a fall onto the shoulder, can also result in a SLAP tear, making it a common injury among athletes and active individuals.
Symptoms of SLAP Tears
The symptoms of a SLAP tear are often unmistakable and can include shoulder pain, instability, and a clicking or popping sound during shoulder movements. These symptoms can impair shoulder function, causing pain and reduced range of motion.
Early recognition of these symptoms allows for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosing SLAP Tears
Diagnosing a SLAP tear of shoulder involves a comprehensive approach that includes patient history, physical examinations, and imaging techniques. This multi-faceted approach ensures an accurate diagnosis, allowing for appropriate treatment planning.
Physical Examination
In a physical examination for a SLAP tear, the doctor reviews the patient’s history and symptoms for signs of shoulder pain or instability. The examination includes specialized tests such as the active compression test, biceps load test II, and Speed’s test, which help in assessing the integrity of the labrum.
These tests aim to elicit responses indicating a labral tear, such as pain or a sense of instability under specific stresses. The physical exam is a critical step in diagnosing SLAP tears, providing valuable insights into the condition.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging techniques are pivotal in diagnosing SLAP tears. While X-rays do not reveal the soft tissues of the shoulder, MRI scans are highly effective in visualizing the labrum and identifying tears with about 80 to 85 percent accuracy. However, MRIs can sometimes miss smaller tears or be unreliable for larger ones.
An MRI arthrogram, involving dye injection into the shoulder, enhances labrum visibility and provides a clearer picture of any damage. These imaging techniques, analyzed by musculoskeletal radiologists, are essential for confirming a diagnosis and planning treatment.
Treatment Options for SLAP Tears
Treatment options for SLAP tears range from non-surgical methods to surgical interventions, depending on the injury’s severity and the patient’s response to initial treatments.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Non-surgical treatments for SLAP tears usually begin with rest and conservative management to prevent further damage. Anti-inflammatory medications, such as NSAIDs, and corticosteroid injections can help reduce pain and inflammation.
Rest and physical therapy are crucial in SLAP tear recovery, enabling the shoulder to heal and regain its range of motion. These treatments can significantly improve the patient’s quality of life without the need for invasive procedures.
Surgical Treatments
Surgical intervention becomes necessary when non-surgical treatments fail to alleviate symptoms. Arthroscopic surgery, a primary method for SLAP repairs, uses minimally invasive techniques to trim or reattach the torn labrum. This approach restores normal shoulder function with shorter recovery times and less pain than open surgery.
The surgeon uses an arthroscope, a tiny camera inserted through small incisions, to visualize and repair the damaged labrum. This precise method ensures that the labrum is properly reattached, allowing for better recovery outcomes.
SLAP Repair Surgery
SLAP repair surgery is a specialized procedure performed with arthroscopic techniques under general anesthesia. This surgery aims to restore the shoulder’s anatomy and function by reattaching the torn labrum to its normal position.
Procedure Overview
SLAP repair involves making small incisions around the shoulder to insert an arthroscope and surgical instruments. The surgeon identifies the tear, trims frayed areas, and reattaches the labrum using sutures anchored into the bone. This minimally invasive approach reduces recovery time and improves outcomes by preserving as much of the shoulder’s natural anatomy as possible.
The surgery’s primary goal is to restore normal shoulder function, enabling the patient to return to regular activities without pain or instability. The benefits of SLAP repair include a more stable shoulder joint and improved movement.
Postoperative Care
Postoperative care is essential for a successful recovery from SLAP repair surgery. Patients generally need to wear a sling for about four to six weeks to immobilize the shoulder and ensure proper healing. Pain management is achieved through prescribed medications and ice application to reduce swelling and discomfort.
During the initial recovery phase, patients should avoid lifting or reaching with the operated arm and follow a structured physical therapy program to regain strength and mobility. Clear communication with the orthopedic team ensures that patients understand their recovery plan and adhere to all postoperative instructions.
Recovery from SLAP Repair Surgery
Recovery from SLAP repair surgery can be lengthy, taking six months to a year. The timeline varies depending on the tear’s severity, the surgical repair’s quality, and patient adherence to rehabilitation protocols.
Rehabilitation Program
Rehabilitation for SLAP repair surgery starts with passive range of motion exercises during the first four weeks post-surgery. Physical therapy then advances to gentle stretching and isometric exercises to maintain muscle tone and prevent stiffness. The goal is to restore shoulder strength and mobility gradually, ensuring a full recovery.
Effective rehabilitation, tailored to individual needs, focuses on achieving maximum function and reducing shoulder pain. This step-by-step approach helps patients regain confidence in using their shoulder without fear of re-injury.
Long-Term Outcomes
Long-term outcomes for SLAP repair surgery are generally positive, with most patients reporting significant improvements in shoulder function and less pain.
Potential risks and complications, such as infection and shoulder stiffness, should be considered and discussed with the surgeon.
Prevention Tips for SLAP Tears
Preventing SLAP tears, especially among athletes and older adults, involves daily stretching and strengthening exercises targeting the shoulder capsule and upper back.
These preventative measures help maintain shoulder blade health and reduce the risk of injury.
Strengthening Exercises
Regular shoulder stretching and strengthening routines are vital for reducing the risk of SLAP injuries. Exercises like lateral raises, external rotations with resistance bands, and scapular stabilization exercises such as lying dumbbell presses can significantly enhance shoulder strength and stability. Plyometric exercises, such as throwing a medicine ball, improve shoulder power and endurance, further protecting against injuries.
A consistent routine of these exercises, supervised by a physical therapist, strengthens the shoulder, improves joint stability, and reduces the risk of future injuries.
Proper Techniques
Proper techniques during sports and physical activities are crucial for preventing SLAP injuries. Proper form, especially during overhead activities, minimizes strain on the shoulder joint and reduces the likelihood of a tear. Proper techniques enhance athletic performance and ensure safer participation in sports.
Athletes should practice these techniques consistently to protect their shoulders and maintain optimal function. This proactive approach helps avoid debilitating injuries and prolong an active lifestyle.
👉Also Read: The Ultimate Guide to Sports Medicine: Enhancing Athletic Performance and Recovery
Don’t Let Shoulder Pain Hold You Back—Schedule a Consultation Today!
If you suspect you have a SLAP tear or are experiencing shoulder pain, don’t wait to take action. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to preventing further damage and restoring your shoulder’s function. At Academy Orthopedics, our experienced team of board-certified orthopedic surgeons is committed to providing the highest quality care, from precise diagnosis to advanced treatment options. Whether you require conservative treatment or minimally invasive arthroscopic surgery, we’re here to help you recover quickly and safely. Contact us today to schedule an appointment to start your journey to a pain-free shoulder.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the recovery time for a SLAP tear?
The recovery time for a SLAP tear varies depending on the severity of the injury and the chosen treatment method. Non-surgical treatments, such as rest and physical therapy, may take a few weeks to several months for noticeable improvement. However, if surgery is required, the healing process typically spans 6 to 12 months.
Post-surgery, patients often wear a sling for 4 to 6 weeks and follow a structured rehabilitation program to regain strength and mobility. Full recovery, allowing a return to normal activities, depends on adherence to recovery protocols and individual healing rates.
What are the risks of leaving a SLAP tear untreated?
If a SLAP tear is left untreated, it can lead to chronic shoulder pain, instability, and a reduced range of motion. Over time, the condition may worsen, potentially causing further damage to the shoulder joint, including rotator cuff injuries or biceps tendon problems. Untreated SLAP tears can also impair daily activities and athletic performance, as the shoulder may become weaker and less stable.
