
The knee is a complex joint, and its functionality heavily relies on the meniscus. This C-shaped piece of cartilage acts as a shock absorber, cushioning the bones and stabilizing the knee joint during movement. The meniscus is made of tough yet flexible connective tissue, allowing it to withstand the pressures of daily activities and sports. It is richly supplied with blood vessels in its outer third, which aids in the healing process, while the inner two-thirds are avascular, making injuries in this area more challenging to heal.
Proper knee function is essential for mobility, and any damage to the meniscus can significantly impact your quality of life. The menisci play a crucial role in distributing weight across the knee joint, reducing the stress on the articular cartilage and preventing wear and tear.
Repairing a torn meniscus is essential for relieving knee pain and restoring mobility. This article explores the causes, symptoms, and effective treatments available to address meniscus tears.
👉Also Read: Recognizing the Signs: How to Tell If You Have Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Repair Meniscus: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatments
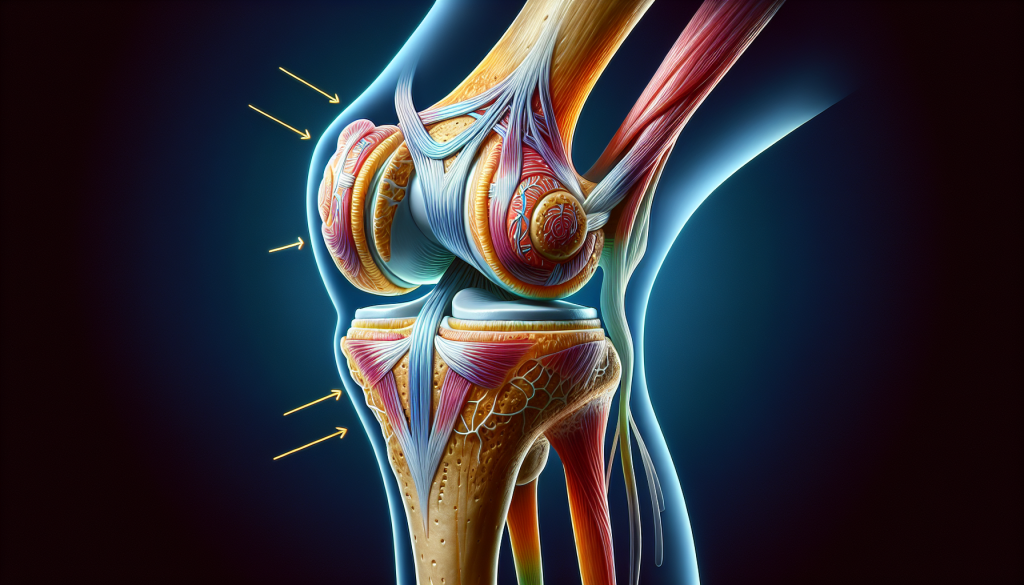
Meniscus tears are among the most common knee injuries, often resulting from an injured knee while underweight, including a lateral meniscus tear and a medial meniscus tear.
Whether you’re an athlete or an active individual, understanding the causes and symptoms of meniscus tears is key to seeking timely treatment.
Causes of Meniscus Tears
Meniscus tears can occur due to various reasons, with acute injuries and degenerative changes being the primary causes.
Common causes of meniscus tears include:
- Forceful twisting or rotation of the knee, especially when weight is applied
- Participation in contact sports, such as football and wrestling
- Involvement in non-contact sports like volleyball and soccer
These activities often involve sudden movements and changes in direction, which can strain the knee and lead to a tear.
Degenerative meniscus tears are more common in older adults, as age-related wear and tear weaken the cartilage, making it more susceptible to injury. Even minor activities, such as squatting or stepping off a curb, can cause a tear in a weakened meniscus. Individuals with a predisposition to arthritis or those who engage in repetitive knee-straining activities are also at an increased risk for tearing a meniscus.
Symptoms of a Torn Meniscus
The symptoms of a torn meniscus can vary widely, but common indicators include:
- Pain
- Swelling
- Stiffness
- Sensations of locking or clicking in the knee
Initially, the pain might be mild, but it can worsen with inflammation, leading to increased swelling and stiffness. These symptoms can significantly impair your ability to move and perform daily activities.
In some cases, individuals may experience mechanical symptoms such as knee locking, where the knee gets stuck in a specific position and cannot be fully straightened or bent. This can be particularly troubling and may require immediate medical attention. Some people might feel pain primarily when the knee is held straight, while others might experience discomfort during activities that involve bending or twisting the knee.
Leaving a meniscus tear untreated can lead to persistent pain and swelling, a decreased range of motion, and long-term complications such as osteoarthritis. Early symptom recognition and prompt medical advice can prevent further damage and speed up recovery.
Diagnosing Meniscus Tears
Diagnosing a meniscus tear involves a combination of physical examinations and imaging tests. Individuals with a torn meniscus may experience a sensation of weakness or instability in the knee, along with clicking or popping sounds. A thorough physical examination is essential for identifying a torn meniscus. Doctors assess knee movement and may ask the patient to perform specific actions like squatting.
An accurate diagnosis is vital for effective treatment planning, determining the tear’s location, severity, and pattern. Surgical options often rely on these assessments to decide the best course of action. Imaging tests complement physical exams by confirming the diagnosis and guiding treatment.
Physical Examination
Healthcare providers diagnose a torn meniscus through medical history and physical examination. During the exam, they evaluate the knee’s range of motion and check for pain or swelling. Specific tests, such as the Thessaly test, are performed by asking the patient to stand on one leg and rotate the knee to assess for pain or locking, indicating a meniscus tear.
The McMurray test is another common method used to detect a torn meniscus. During this test, the knee is bent and manipulated while the patient lies on their back to check for meniscal damage. These examination techniques are crucial for diagnosing meniscus tears and formulating an effective treatment plan.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests are essential for visualizing internal injuries and diagnosing meniscus tears. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is regarded as the most effective method for visualizing meniscal tears, distinguishing them from other knee pathologies.
Such non-invasive tests allow healthcare providers to accurately assess the injury’s extent and guide the treatment process.
Treatment Options for Meniscus Tears
The treatment of a meniscal tear depends on several factors, including:
- Symptoms
- Age
- General health
- Severity of the condition
- Type, size, and location of the tear
- Patient’s age and activity level
In some cases, conservative treatment suffices, while others may require surgery to alleviate symptoms and restore knee function.
Treatment options range from non-surgical methods, such as physical therapy and medications, to surgical interventions like meniscus repair or debridement. Knowing the available treatment options and potential outcomes is crucial for making informed decisions about knee health.
👉Also Read: The Ultimate Guide to Sports Medicine: Enhancing Athletic Performance and Recovery
Non-Surgical Treatments
Non-surgical treatments for meniscus tears aim to relieve pain and reduce swelling. Here are some recommended methods:
- Resting the knee and avoiding aggravating activities to facilitate healing.
- Applying ice to the knee to alleviate pain and swelling.
- Utilizing the RICE method (rest, ice, compression, and elevation) for managing symptoms.
- Taking over-the-counter pain medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, to provide relief from knee pain associated with a meniscus tear.
By following these treatments, you can help manage the symptoms of a meniscus tear effectively.
Physical therapy is a crucial aspect of non-surgical treatment. It helps regain knee motion, strength, and overall function. Strengthening the muscles around the knee provides better support and alleviates stress on the meniscus, facilitating recovery and preventing further injuries.
Surgical Treatments
When conservative treatment fails to alleviate symptoms, surgical options may be considered. Surgical treatments for meniscus tears include meniscectomy (meniscus removal), meniscus repair, and meniscus replacement. Arthroscopic surgery involves inserting a small camera through a tiny incision, allowing your surgeon to view the inside of your knee on a large screen. The surgery is then performed using specialized instruments inserted through additional small incisions.
Meniscectomy (Meniscus Removal): This procedure involves removing the damaged portion of the meniscus. It is typically recommended when the tear is in a part of the meniscus with poor blood supply, making healing unlikely. By removing the torn section, the surgeon aims to alleviate pain and restore knee function. Recovery is usually quicker compared to other surgical options, but it may increase the risk of arthritis in the long term.
Meniscus Repair: In cases where the tear occurs in an area with good blood supply, the meniscus may be repaired using sutures or other fixation methods. This procedure preserves the meniscus and its function, promoting long-term joint health. Recovery takes longer than a meniscectomy, as the meniscus needs time to heal properly.
Meniscus Replacement: For severe cases where most or all of the meniscus is damaged, a meniscus replacement may be considered. This can involve using donor tissue (allograft) to replace the damaged meniscus. It’s usually reserved for younger, active patients who have failed other treatments. Recovery is extensive and requires physical therapy, but it can help restore knee function and reduce pain in the long term. This is a very uncommon treatment technique, however.
Post-Surgery Care
Managing pain and swelling is essential in the immediate aftermath of meniscus surgery to support recovery. Pain management may include prescribed medications and over-the-counter pain relievers to ensure comfort. Swelling can be managed by elevating the leg and using ice packs to reduce inflammation after surgery.
Following the prescribed care plan and attending follow-up appointments with the surgeon help monitor progress and address any complications early on.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy after meniscus surgery focuses on regaining knee motion, strength, and overall function. Therapy often starts with gentle range-of-motion exercises to restore knee mobility after surgery. Strengthening exercises are essential to rebuild muscle support around the knee joint after surgery. Strengthening the quadriceps is a primary goal in physical therapy, helping maintain knee extension and prepare for weight-bearing activities.
Therapists may use modalities such as ultrasound or electrical stimulation to aid recovery during physical therapy. Patients may need to use crutches and wear a brace after surgery to offload the knee and protect the surgical site. Early physical therapy sessions may involve discomfort but are essential to prevent knee stiffness and facilitate recovery.
Potential Complications
An untreated torn meniscus can lead to additional knee cartilage damage. Chronic pain from an untreated meniscus tear can cause muscle weakness around the joint. Improper healing of a meniscus tear can result in persistent knee pain. This discomfort may persist over time if not addressed adequately.
In the long term, untreated meniscus tears increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis, a condition that causes joint pain and stiffness. Knee instability from an untreated torn meniscus can lead to permanent joint damage, increasing the risk for arthritis.
Recognizing and treating meniscus tears promptly prevents these complications and ensures better knee health.
Preventing Meniscus Tears
Preventing meniscus tears is essential for maintaining knee health and avoiding long-term complications. Dynamic stretching before physical activities reduces injury risk and eases post-activity soreness. Proper warm-up routines with stretching and strengthening exercises prepare the knee for physical activities, minimizing injury risks.
Strengthening the legs and core muscles distributes pressure away from the meniscus and lowers the risk of injuries. Engaging in specific exercises, such as mini squats and hamstring curls, can strengthen the muscles around the knee and help reduce the risk of meniscus injuries.
Avoidance of high-impact activities and exercises that involve twisting motions can significantly lower the chances of sustaining a meniscus tear. Strengthening the quadriceps and hamstring muscles is crucial, as these muscles support the knee joint and help absorb shocks during movement. Taking these preventive measures can protect your knees and maintain their health.
👉Also Read: Where Does It Hurt? Why an Orthopedic Doctor Asks These Questions
Take the First Step Toward Pain-Free Movement—Contact Academy Orthopedics Today!
If you’re experiencing knee pain or suspect a meniscus tear, don’t wait for the symptoms to worsen. At Academy Orthopedics L.L.C., our dedicated team of experienced orthopedic surgeons is here to provide personalized and effective care, ensuring you receive the best treatment options available.
Whether it’s a conservative approach or an advanced surgical procedure like arthroscopic meniscus repair, we tailor our services to meet your needs and help you regain mobility. Contact us today to schedule a consultation at one of our convenient locations in Cumming, Buford, or Duluth, and take the first step towards a pain-free, active lifestyle. Your path to recovery starts with Academy Orthopedics—call us at (770) 271-9857 or book an appointment online now!
