If you’re dealing with a ganglion cyst, you probably want to know the best ganglion cysts treatment options to relieve pain and discomfort. Ganglion cysts can be bothersome, but several treatments are available to help manage them. In this article, we’ll explore both non-surgical and surgical treatments for ganglion cysts, as well as tips for managing symptoms at home.
Key Takeaways
- Ganglion cysts are benign fluid-filled lumps often found on the wrist, causing discomfort and varying symptoms, with non-surgical treatments as the first line of management.
- Common non-surgical therapies include observation, immobilization, aspiration, and steroid injections, while surgical options like open excision and arthroscopic surgery are reserved for more severe cases.
- Proactive management techniques, such as wrist exercises and lifestyle adjustments, play a key role in preventing recurrence and maintaining a higher quality of life for individuals with ganglion cysts.
If you’re experiencing discomfort or have noticed a mass on your wrist or hand, it’s important to consult a specialist. At Academy Orthopedics, our expert team is here to diagnose and treat ganglion cysts, offering both non-surgical and surgical options tailored to your needs. Don’t let uncertainty or pain linger—schedule an appointment today to explore the best treatment plan for you and get back to your normal activities with confidence.
👉Also Read: Recognizing the Signs: How to Tell If You Have Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Understanding Ganglion Cysts
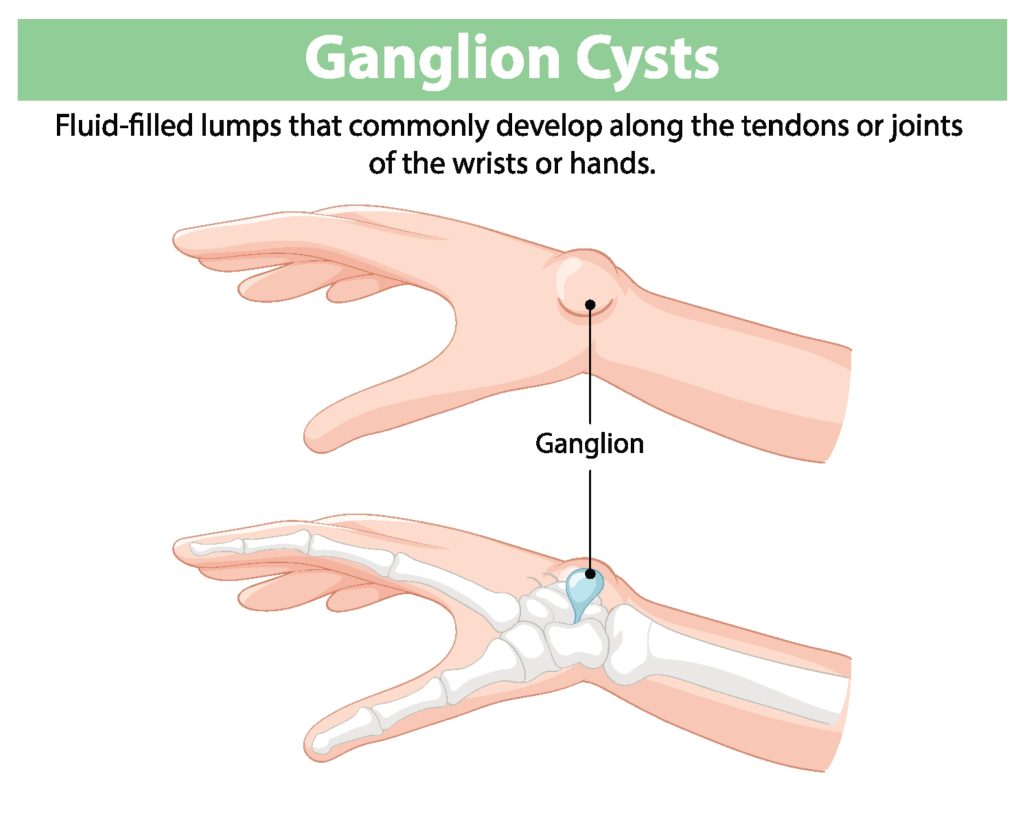
Ganglion cysts are fluid-filled lumps that form beneath the skin, most commonly on the dorsal (top) or volar (palm) sides of the wrist, as well as on the palm side of the hand. These cysts are generally benign and not cancerous, which means they do not pose a serious health risk. However, their appearance can be unsightly, and they can cause discomfort or pain, particularly if they press on nearby nerves.
The symptoms of ganglion cysts can vary. Here are some common symptoms:
- Pain
- Tenderness
- Muscle weakness in the affected area
- Unsightly appearance of the cyst
These cysts can develop in individuals of any age but are most prevalent among those aged 15 to 40. Interestingly, females are three times more likely to develop ganglion cysts than males.
Ganglion cysts can range in size, including a large cyst, and may fluctuate, growing larger or smaller over time. Despite their benign nature, understanding many ganglion cysts symptoms and potential impact on daily activities is essential for seeking appropriate treatment and relief.
Causes of Ganglion Cysts
Ganglion cysts typically arise from a small tear in the tissue surrounding a joint or tendon sheath, which causes a bulge filled with fluid to form. This fluid filled cysts can develop due to a variety of factors. One prominent theory suggests that these cysts result from repetitive micro-injury or trauma, which leads to the degeneration of connective tissue. As the tendon sheath deteriorates, a cyst can form, filled with a jelly-like fluid.
Another possible cause of ganglion cyst involves the herniation of synovial tissue, which is the lubricating tissue around joints. This herniation allows the fluid to escape and accumulate, forming a cyst. Additionally, mucinous degeneration, which involves changes in the connective tissue, is also thought to contribute to the development of causes ganglion cysts called mucous cysts.
Although wrist sprains or direct trauma to the wrist are commonly associated with cyst ganglion formation, the exact cause can sometimes remain unknown. Recognizing these potential causes aids in both prevention and effective management of the condition.
Diagnosing Ganglion Cysts
A healthcare provider can diagnose ganglion cysts diagnosed through a thorough evaluation of your medical history and a physical examination, including applying pressure to the affected area to detect tenderness and assess the cyst’s impact on nearby structures. This helps distinguish ganglion cysts from other conditions.
Ultrasound and MRI are useful imaging techniques for further evaluation. Ultrasound is especially effective at identifying hidden ganglion cysts and distinguishing them from solid tumors, while MRI scans offer detailed images of soft tissues, aiding in the identification of the cyst and any associated injuries.
Accurate diagnosis is vital for effective treatment and ruling out other conditions with similar symptoms. A clear understanding of the diagnostic process helps patients confidently approach their healthcare providers.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Non-surgical treatments are usually the first approach for asymptomatic or minimally discomforting ganglion cysts treated. These include observation, immobilization, aspiration, and steroid injections, each providing different levels of relief and recurrence potential in ganglion cyst treatment.
Observation
Observation is often used to manage asymptomatic ganglion cysts. Monitoring the cyst over time can avoid unnecessary interventions and allow it to potentially regress on its own, especially for those without significant pain or discomfort.
Observation helps patients avoid risks and complications of invasive treatments. Regular check-ups ensure prompt addressing of any changes in the cyst’s size or symptoms, offering peace of mind.
Immobilization
Using a brace or splint to limit joint movement, immobilization helps alleviate pain and reduce cyst size by minimizing movement and relieving pressure on nearby nerves.
Wrist braces or compression wraps effectively reduce cyst size and provide support during daily activities, making this simple method a popular choice for managing cyst presses symptoms.
Aspiration
Aspiration involves using a needle to drain the cyst fluid, offering temporary symptom relief. However, the cyst’s root remains, resulting in a high recurrence likelihood of around 50%.
Despite being temporary, aspiration can provide immediate pain and discomfort relief. It is often performed in a clinical setting and can be combined with other treatments for better effectiveness.
Steroid Injections
Steroid injections, another non-surgical option, reduce inflammation around the cyst, potentially decreasing its size and providing pain relief.
Useful for managing symptoms and preventing cyst interference in daily activities, these injections offer significant temporary relief and are often combined with other treatments, though they do not guarantee permanent resolution.
Surgical Treatment Options
When non-surgical treatments are inadequate or the cyst significantly impacts daily activities, surgical intervention might be necessary. Options include open excision and arthroscopic surgery, each with unique benefits and recovery considerations.
Open Excision
Open surgical excision, a traditional method, involves making an incision to completely remove the cyst and its stalk, minimizing the chances of recurrence.
Although effective, open excision requires a recovery period with specific post-operative care instructions to ensure optimal healing.
Arthroscopic Surgery
Arthroscopic surgery, a less invasive option, uses small instruments and a camera to remove the cyst through a tiny incision, minimizing tissue damage and often resulting in quicker recovery times compared to open excision.
Using a camera allows precise cyst and stalk removal, reducing recurrence likelihood and complications, making it a beneficial option for those seeking minimally invasive surgery.
Post-Operative Care and Recovery
Recovery from ganglion cyst surgery typically takes 2 to 6 weeks, depending on the method used and individual healing rates. Patients may experience swelling and discomfort initially, with physical therapy often recommended to aid healing.
Swelling can persist for up to 3 months post ganglion cyst removal surgery, but recurrence rates are relatively low (around 10-15%). Proper post-operative care ensures a smooth recovery and minimizes recurrence risk.
Managing Symptoms at Home
Several strategies can help manage ganglion cyst symptoms at home. Applying heat or cold packs provides temporary pain relief, while wrist braces or wraps alleviate stress on wrist joints during repetitive activities, significantly improving daily comfort and function.
Targeted wrist exercises, such as wrist curls and grip-strengthening activities, enhance hand and wrist stability and reduce cyst formation likelihood. Ergonomic tools and supports minimize wrist strain, aiding in symptom management and prevention.
Regular breaks during repetitive tasks reduce wrist strain and lower cyst recurrence chances. Adopting these home management strategies helps manage symptoms effectively and maintain a higher quality of life.
Preventing Recurrence
Preventing ganglion cyst recurrence requires wrist care and avoiding repetitive strain. Lifestyle changes, like reducing repetitive joint movements and avoiding heavy lifting, significantly lower the risk of new cyst formation.
Consulting a healthcare professional to address underlying joint conditions offers tailored strategies to minimize recurrence risk. Proactive steps help manage and prevent ganglion cyst reappearance.
When to See a Doctor
Persistent symptoms like pain or discomfort warrant consultation with a healthcare professional. If a ganglion cyst affects daily activities or job performance, seeking medical advice is recommended.
Consult a doctor if the cyst is painful or limits movement. A medical evaluation ensures the lump is not indicating a different condition and helps determine the most appropriate treatment options.
Surgical intervention is recommended for ganglion cysts causing persistent symptoms like pain or discomfort, or for cosmetic reasons. Knowing when to seek professional help ensures timely and effective treatment.
👉Also Read: Choosing the Right Specialist: What Doctor Should I See for Shoulder Pain?
Experience Expert Ganglion Cyst Treatment at Academy Orthopedics
Don’t let a ganglion cyst limit your daily activities. At Academy Orthopedics, our expert hand and wrist surgeons are dedicated to providing personalized treatment options that deliver lasting relief. Whether you’re seeking non-surgical approaches like utilizing splint support or immobilization, or considering surgical intervention such as open excision or arthroscopic surgery, we have the expertise to guide you towards a pain-free and functional outcome.
Schedule a consultation today at 770-271-9857 to discuss your specific needs and learn more about how we can help you overcome the discomfort and limitations caused by your ganglion cyst. Our goal is to restore your hand and wrist health and enable you to live life to the fullest.
