
Ever woken up to a stubborn finger stuck in a bent position? Trigger finger, a condition characterized by the finger getting locked in a bent position often manifests with discomfort and limited mobility. The ring finger and thumb are frequently impacted, but the trigger finger can affect any digit. When the thumb is affected, it is specifically called trigger thumb.
At Academy Orthopedics, we blend professional expertise with compassionate care to provide comprehensive solutions for trigger finger and its associated challenges.
👉Also Read: How Does Trigger Finger Occur?
What is Trigger Finger?
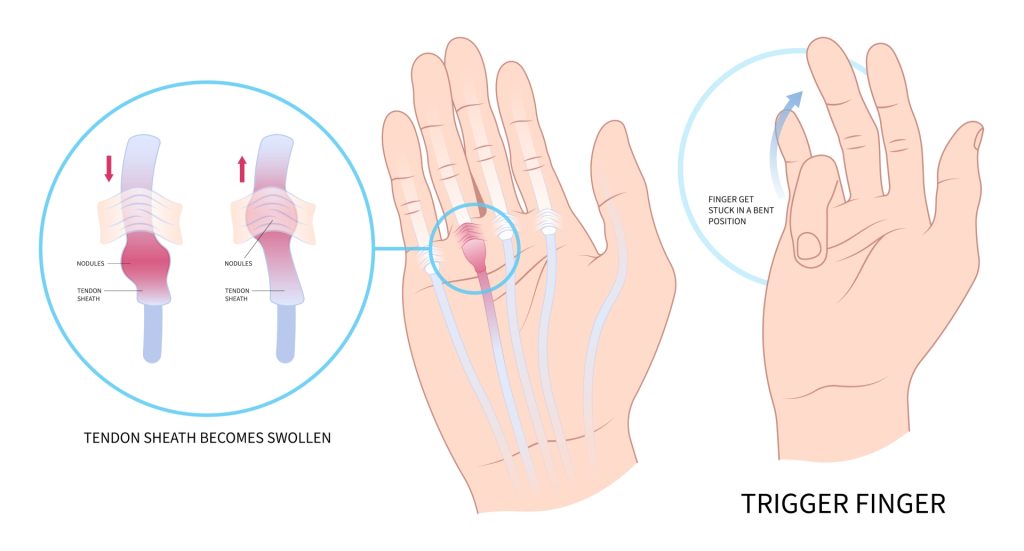
Trigger finger is a condition where a finger gets stuck in a bent position, then snaps straight, much like pulling and releasing a trigger. It differs from the trigger thumb, which affects the thumb in the same manner.
Both conditions result from inflammation or narrowing of the tendon sheath, the protective covering of tissue that facilitates smooth tendon movement. When the sheath becomes irritated, it hinders the tendon’s glide, causing the finger or thumb to lock or catch.
Common Symptoms of Trigger Finger
Symptoms of trigger finger include stiffness, particularly in the morning, and a popping or clicking sensation when moving the affected digit. The finger or thumb may lock in a bent position and suddenly snap or straighten out, causing pain or discomfort. This condition can affect any digit, including the thumb, and is more common in fingers used repetitively.
Trigger Finger Risk Factors and Causes
Trigger finger is often caused by repetitive gripping or movements that strain the tendons in the fingers and thumb. This repetitive strain can lead to inflammation of the tendon sheaths, causing the finger to catch or lock.
Factors contributing to the risk include participating in activities that require prolonged gripping. Additionally, health conditions like Diabetes, obesity, Sarcoidosis, Amyloidosis, Hypothyroidism, and Rheumatoid Arthritis can heighten susceptibility to trigger finger.
Additionally, women and individuals over the age of 40 are more likely to develop trigger finger, highlighting the impact of both biological and lifestyle factors on its occurrence.
Identifying and Diagnosing Trigger Finger
Diagnosing the trigger finger primarily involves recognizing the characteristic symptoms, such as stiffness, locking, and a clicking sensation in the affected finger or thumb. Orthopedic surgeons conduct a thorough physical examination, focusing on the range of motion, tenderness, and the presence of nodules on the tendon.
While X-rays and other diagnostic tools are not typically needed to diagnose trigger finger, they may be used to rule out other conditions that could cause similar symptoms, ensuring an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
👉Also Read: How to Find the Best Center for Orthopedics Near You
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
For mild cases of trigger finger, nonsurgical approaches can be highly effective. These include rest and activity modification to reduce strain on the affected digit.
Over-the-counter medications, such as anti-inflammatory drugs, can alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
Splinting the affected finger, especially at night, can help prevent it from locking, allowing the tendon sheath to rest and heal.
Steroid injections are another key option; by delivering a potent anti-inflammatory directly into the swollen tendon sheath, they can significantly reduce swelling and improve movement.
This combination of treatments often provides relief and prevents the condition from worsening.
Advanced Treatment: Trigger Finger Release Surgery
Trigger finger release surgery is recommended when nonsurgical treatments fail to alleviate symptoms. Trigger finger surgery is a minor procedure that involves cutting the affected tendon sheath to allow the tendon to move freely without catching it.
Surgery is typically advised for severe cases where the finger remains locked in a bent position or pain persists despite other treatments. The surgical procedure itself is usually performed under local anesthesia on an outpatient basis, allowing for a quick return home.
Read more about local only (WALANT) surgery, which we specialize here at Academy Orthopedics.
Recovery involves rest and possibly physical therapy to regain full motion and strength. Most patients experience significant improvement, with minimal downtime and a swift return to daily activities.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Post-surgery recovery for trigger finger generally spans a few weeks, during which the protective sheath around the tendon heals. It’s crucial to follow a tailored rehabilitation program, including stretching exercises, to restore flexibility and prevent stiffness. These exercises gradually improve the range of motion and strength of the affected finger.
Lifestyle Changes and Preventive Measures
To prevent trigger finger, identifying and avoiding activities that strain the fingers is key. Lifestyle adjustments, such as taking frequent breaks during repetitive tasks and using ergonomic tools, can significantly reduce the risk of recurrence.
It’s also recommended to practice exercises that strengthen and stretch the hand muscles, promoting flexibility. For those required to use forceful hand movements, adopting techniques that distribute pressure more evenly across the palm and hand can help. These measures not only prevent trigger finger but also contribute to overall hand health.
👉Also Read: How to Find an Orthopedist in Duluth, GA
Take Control of Your Trigger Finger Today with Academy Orthopedics
If you’re experiencing symptoms of trigger finger or seeking comprehensive orthopedic care, don’t hesitate to reach out to Academy Orthopedics. We have a board-certified Orthopedic Hand Surgeon on staff and our team of experienced orthopedic surgeons is here to guide you through every step of your treatment journey and help you regain optimal hand function and comfort. Take the first step towards relief and schedule your consultation with Academy Orthopedics today. Your hands deserve the best care possible.
