Wrist tendonitis often stems from repetitive movements, overuse, sports activities, or sudden trauma. This article explores these wrist tendonitis causes in detail to help you understand and prevent this condition.
Key Takeaways
- De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is a type of wrist tendonitis predominantly affecting the thumb side of the wrist, often caused by repetitive movements, overuse injuries, sports activities, and direct trauma.
- Common risk factors for wrist tendonitis include occupational activities with repetitive wrist movements, certain medical conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and obesity, and demographic attributes such as age and gender.
- Preventive measures such as ergonomic adjustments, taking regular breaks, and performing strengthening exercises can significantly reduce the risk of developing wrist tendonitis, while treatment options range from home remedies and physical therapy to medical interventions and surgery for severe cases.
Are you struggling with De Quervain’s tenosynovitis or other musculoskeletal issues? At Academy Orthopedics, we provide expert care for a variety of orthopedic conditions, including De Quervain’s tenosynovitis. Our specialized services range from General Orthopedic Surgery to Hand & Upper Extremity treatments and Sports Medicine. Our team of board-certified surgeons, is dedicated to delivering personalized care that prioritizes your comfort and promotes optimal recovery.
Ready to regain your mobility and improve your quality of life? Don’t wait any longer—schedule an appointment with our experts today. Explore more about our services and book your visit at our convenient locations in Cumming, Buford, or Duluth, GA.
👉Also Read: Understanding Wrist Ligaments: A Comprehensive Guide
What is Wrist Tendonitis?
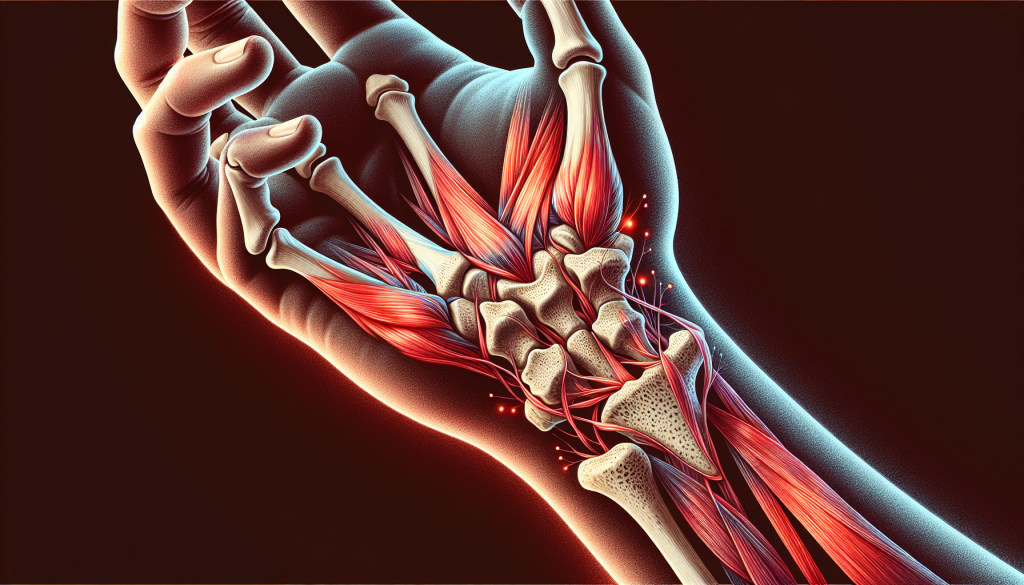
Wrist tendonitis, often referred to as tendinitis, involves inflammation in the tissues that connect the muscles of the forearm to the hand bones. Overuse or injuries typically trigger this condition, which results in significant discomfort and functional wrist and hand limitations. The tendons, which are thick, flexible tissues, play a crucial role in facilitating movement and providing stability. A thin, soft tissue sheath known as the tendon sheath covers them, facilitating smooth gliding.
There are about six tendons in the wrist. These tendons assist in controlling movements of the wrist, hand, and fingers. Among these, the extensor pollicis brevis and the abductor pollicis longus are two tendons located on the thumb side of the wrist. Inflammation and swelling, a condition known as De Quervain’s tenosynovitis, predominantly affects these tendons. This specific type of tendonitis is common and can significantly impact thumb and wrist movements.
When the tendons in the wrist become inflamed, it can lead to symptoms such as pain, swelling, and reduced range of motion. The inflammation can cause the tendon to swell and become irritated, leading to a cycle of pain and discomfort that can be challenging to break without proper intervention. Understanding the causes of wrist tendonitis is the first step in managing and preventing this painful condition.
Common Causes of Wrist Tendonitis
Common causes of wrist tendonitis include:
- Repetitive movements
- Overuse injuries
- Sports activities
- Sudden trauma
Each of these factors can place excessive strain on the wrist tendons, leading to inflammation and pain.
Identifying and understanding these causes enables individuals to take proactive measures, safeguarding their wrists and reducing tendonitis risk.
Repetitive Movements
Repetitive movements are a significant risk factor for developing wrist tendonitis. Activities such as:
- Typing
- Lifting a baby
- Hammering
- Knitting
- Playing video games
All involve repetitive motions that can strain the wrist tendons. In time, these repetitive tasks can instigate inflammation and tendon swelling, resulting in wrist pain and discomfort. For instance, typing or using a computer mouse for prolonged periods can contribute to wrist tendonitis due to the constant repetitive motions involved.
The strain from repetitive movements doesn’t just affect the tendons; it can also impact the muscles and other structures in the hand and wrist. Writing with a pen and paper repetitively or performing tasks like knitting can lead to similar issues. Individuals can help cut the risk of wrist tendonitis by being aware of daily repetitive movements and taking frequent breaks.
Overuse Injuries
Overuse injuries, such as those caused by heavy lifting or prolonged periods of wrist activity, can also lead to wrist tendonitis. When the wrist is subjected to excessive strain without adequate rest, the tendons can become inflamed and irritated.
Balancing rest with activity and using joint protection techniques is key to preventing overuse injuries in the wrist joint. These strategies can help minimize the risk of developing wrist tendonitis and promote tendon healing.
Sports Activities
Sports activities that require repetitive wrist movements, such as tennis and golf, are common culprits of wrist tendonitis. Athletes who engage in these sports often perform repetitive motions that can strain the wrist tendons. The frequent grasping and gripping involved in these activities can lead to inflammation and pain in the wrist.
Implementing proper training techniques and taking breaks during sports activities can help lessen the chance of tendon injuries.
Trauma and Injury
Direct trauma to the wrist, such as a blow or fall, can cause significant damage to the tendons and lead to inflammation. An acute injury can cause the tendon to rub against bone, leading to irritation and wrist swelling. Such trauma can cause immediate pain and functional limitations, necessitating prompt medical attention to avert further injury and promote healing.
👉Also Read: Tailored Treatments and Compassionate Care: How To Find The Best Orthopedic Surgeon
Risk Factors for Developing Wrist Tendonitis
Several risk factors can elevate the likelihood of developing wrist tendonitis. These include occupational activities that involve repetitive wrist movements, certain medical conditions, and demographic attributes such as age and gender.
Comprehending these risk factors aids individuals in taking preventive measures and seeking early intervention if symptoms surface.
Occupational Risks
Certain professions that are more prone to wrist tendonitis due to the repetitive nature of their tasks include:
- Writers and journalists, who often spend long hours typing
- Hairdressers, who frequently use scissors and clippers
- Individuals who perform housework, which involves repetitive wrist actions
These individuals can mitigate their risk of tendon injuries by incorporating ergonomic adjustments and taking regular breaks.
Another high-risk occupation includes those who perform manual labor, such as construction workers. These jobs often require heavy lifting and repetitive wrist movements, increasing the likelihood of tendon strain and inflammation. Ensuring proper technique and using supportive equipment can help mitigate these risks.
Medical Conditions
Medical conditions like diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis and obesity can also increase the risk of developing wrist tendonitis. Rheumatoid arthritis leads to inflammation in the joints, which can extend to the tendons, causing pain and swelling. Obesity adds additional stress on the tendons, making them more susceptible to injury and inflammation.
Proper medical care management of these underlying conditions can help lower the risk of wrist tendonitis.
Age and Gender
Middle-aged women are particularly susceptible to De Quervain’s tenosynovitis, a common form of wrist tendonitis. This condition affects the tendons near the thumb and is often caused by repetitive thumb and wrist movements. It is most prevalent in pregnant and middle-aged women due to hormonal changes and increased wrist usage.
Comprehending this demographic risk can aid in early detection and preventive care.
Symptoms of Wrist Tendonitis
Wrist tendonitis manifests through a variety of symptoms, including:
- Irritation and pain in the tendons
- Wrist pain that worsens with movement, making it difficult to perform everyday tasks
- Swelling around the wrist, which can lead to tenderness when touching the affected area
- Inflammation that causes the tendon to swell, resulting in painful swelling and reduced range of motion
Detecting these symptoms early is vital for effective treatment and prevention of further complications.
In addition to pain and swelling, individuals with wrist tendonitis may experience wrist weakness and difficulty moving the wrist. These symptoms can significantly impact daily activities and overall quality of life. The pain and discomfort are often aggravated by repetitive wrist movements, emphasizing the importance of addressing these symptoms promptly to prevent chronic issues. Early recognition of wrist tendonitis signs can result in more effective treatment and quicker recovery.
Diagnosis of Wrist Tendonitis
Diagnosing wrist tendonitis involves:
- A thorough review of the patient’s medical history
- A physical examination
- Inquiring about the onset of pain, any recent trauma, and symptoms such as muscle spasms and strength loss
- In some cases, imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI might be ordered to confirm tendon injuries and check for other conditions like fractures or arthritis.
Physical Examination
During a physical examination, the doctor will:
- Check for pressure tenderness, flexibility, and range of motion in the wrist and forearm
- Apply gentle pressure to different areas of the wrist, hand, and forearm to identify tender spots and assess the severity of the inflammation
- Perform specialized manual tests to help determine the location and extent of tendonitis.
The doctor may ask the patient to perform certain movements to evaluate the wrist’s functionality and identify any limitations. These movements may include:
- Flexion: Bending the wrist forward
- Extension: Bending the wrist backward
- Radial deviation: Moving the wrist towards the thumb side
- Ulnar deviation: Moving the wrist towards the pinky side
Swelling and bruising are also checked during the examination, as these symptoms can provide additional clues about the condition.
A thorough physical examination aids in accurate diagnosis and effective treatment plan formulation.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests like MRI or ultrasound are sometimes necessary to confirm the diagnosis of wrist tendonitis. An MRI can provide detailed images of the tendons, bones, and cartilage around the wrist, helping to identify any abnormalities. A musculoskeletal ultrasound is particularly useful for closely examining the soft tissues in the hand and wrist.
These imaging tests can exclude other conditions and provide a detailed image of the injured tendon, assisting in creating a suitable treatment plan for tendon injuries.
Preventive Measures

Preventing wrist tendonitis involves taking proactive steps to reduce strain on the wrist tendons. Ergonomic adjustments, regular breaks, and strengthening exercises are key measures that can help protect the wrist and prevent the development of tendonitis.
Incorporating these preventive strategies into daily routines allows individuals to reduce the risk of tendon injuries and uphold wrist health.
Ergonomic Adjustments
Ergonomic adjustments in the workplace can significantly reduce the risk of developing wrist tendonitis. Some key adjustments to consider include:
- Adjusting the height and position of the desk and chair to keep the wrist in a neutral position
- Using an ergonomic keyboard and mouse to reduce strain
- Using a wrist rest for additional support
These adjustments can help reduce pain, minimize stress on the tendons, and promote a more comfortable and ergonomic work environment.
Guaranteeing a workstation layout that allows for fluid arm movements is also vital. Poor ergonomics can lead to repetitive wrist movements, increasing the risk of tendonitis. Making these simple adjustments enables individuals to craft a more comfortable and wrist-friendly work environment, aiding in tendon injury prevention.
Regular Breaks
Regular breaks during repetitive tasks are critical for averting tendon overuse. Frequent breaks, ideally every 20-30 minutes, can help minimize wrist strain and prevent the development of tendonitis. Even micro-breaks of 1-2 minutes can be beneficial, allowing the wrist tendons to relax and recover.
Stretching during these breaks aids in maintaining flexibility and lowering the risk of tendon injuries. Alternating tasks can also help avoid repetitive strain on the wrist.
Strengthening Exercises
Strengthening exercises play a vital role in wrist tendonitis prevention. Specific wrist exercises, such as wrist curls with light weights and resistance band exercises, can strengthen the tendons and improve muscle endurance. Additionally, finger stretches can help maintain overall hand and wrist health, reducing the risk of inflammation and injury.
Consulting with a physical therapist for a tailored exercise program can further enhance wrist strength and flexibility, providing long-term protection against tendonitis.
👉Also Read: Where Does It Hurt? Why an Orthopedic Doctor Asks These Questions
Treatment Options for Wrist Tendonitis
When it comes to treating wrist tendonitis, a range of options is available, from home remedies and physical therapy to medical interventions and surgery. The treatment plan often depends on the severity and type of tendonitis, aiming to relieve pain and reduce inflammation while promoting tendon healing.
Early treatment can stop the condition from deteriorating and aid in more effective wrist heals.
Home Remedies
Home remedies are often the first line of defense against wrist tendonitis. Here are some home remedies you can try:
- Evading activities that exacerbate pain and swelling is vital for symptom management and tendon healing.
- Applying ice to the affected area several times a day can help reduce swelling and alleviate pain.
- Taking anti-inflammatory medications, such as ibuprofen, can further manage pain and reduce inflammation.
- Use of a thumb spica wrist brace
These self-care measures can effectively help in treating tendonitis for mild cases.
Physical Therapy
Focusing on exercises that promote tendon healing and improve wrist mechanics, physical therapy is a cornerstone in wrist tendonitis treatment. Strengthening exercises for the wrist and arm, including the shoulder and elbow, are integral to this approach, helping to alleviate symptoms and prevent future injuries. Techniques such as bracing and splinting can immobilize the wrist, allowing the tendons to rest and heal properly.
Combining exercises with immobilization techniques offers a comprehensive approach to managing wrist tendonitis. Physical therapy can significantly diminish pain and inflammation by addressing both the symptoms and underlying causes, resulting in a quicker and more effective recovery. Regular sessions with a physical therapist can help maintain progress and ensure proper wrist mechanics.
Medical Interventions
Medical interventions may be necessary for more severe cases of wrist tendonitis. Steroid injections can be administered to reduce severe inflammation and pain. Another advanced treatment option is Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) injections, which use growth factors from the patient’s own blood to promote tendon healing.
Typically, these interventions are considered when other treatments have not yielded sufficient relief.
Surgery
As a last resort for treating wrist tendonitis, surgery is generally considered for cases where non-surgical treatments have failed to alleviate symptoms. Surgical procedures may involve making a small incision in the wrist to remove inflamed tissues or release pressure from tight tendon sheaths. These surgeries can be performed under local anesthesia for patient ease and comfort.
Typically, the recovery time after surgery is less than 6-8 weeks, with most patients experiencing notable pain relief and improved wrist function.
👉Also Read: At Home Remedies for Hand and Wrist Tendonitis
Contact Academy Orthopedics
If you suspect you have wrist tendonitis and home remedies aren’t providing relief, it might be time to seek professional help. Our team of orthopedic specialists at Academy Orthopedics is ready to assist you. Persistent pain or swelling in the wrist warrants a consultation to prevent further complications and promote proper healing.
Feel free to contact us for a comprehensive evaluation and a personalized treatment plan.
